How to Contribute to the Docs¶
Warning
Pull Requests will only be accepted if source files have correct .rst formatting and Sphinx directives. Learn more at sphinx-doc.
Web¶
This is the easiest way to contribute. You don’t need to know exactly how git works, you just need to be able to interact with Github’s web interface. Before you can do anything below, you must login to Github or create an account. Afterwards contributing is as simple as following these steps:
Fork
- You can’t edit the repository directly because the master branch is protected. You have to make a fork where your edits are made that will later be merged back into the master branch if your edits are acceptable. Navigate to the Documentation Repository on Github and click the Fork button in the upper right corner:

Add a file
- Adding a file is also really simple. In each directory listing, there is a
+symbol that you can press to create a new directory or file.

- Adding a file is also really simple. In each directory listing, there is a
Edit a file
- Just choose a file you want to edit by clicking on it in the listing:
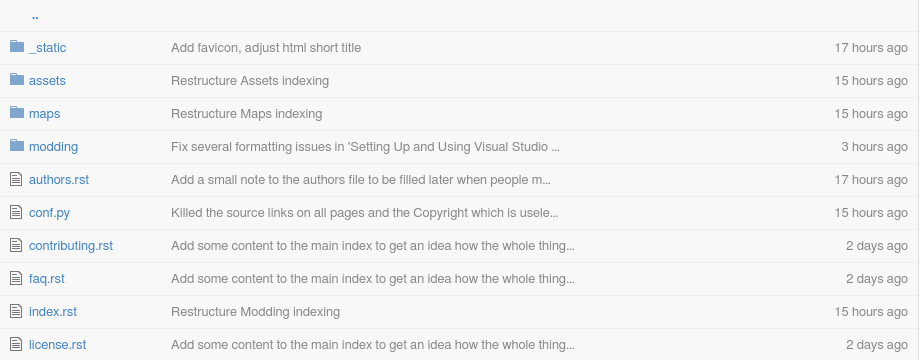
- Then click on the edit pencil in the upper right corner of the file:
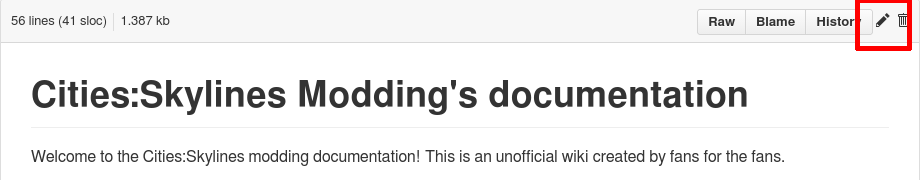
- Commit your changes with a good comment that explains what you did:
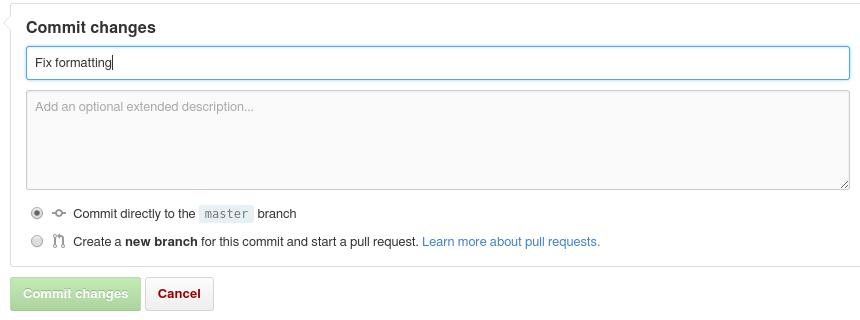
Make a Pull Request
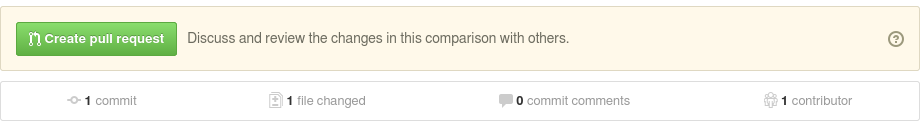
- Compare and Review

- Double check that all of your committed changes are good and conform to RST formatting. Remember, bad formatting will NOT be accepted. If everything looks ok and you’re sure your commits can be merged, go ahead and press the Create Pull Request Button:
Local¶
This method assumes you have some knowledge of the command line and git.
First Time
- Fork the repo like above.
cd /some/empty/directory # Remember that you can get this link from the sidebar on GitHub git clone https://github.com/<your name>/Docs.git cd Docs
All of the source files are in
docs/source. Use your favorite editor to make changes. When you’re done:git add some/file/you/changed git commit -m "Useful commit message explaining what you changed" git pushBack on GitHub, make a Pull Request.
Advanced¶
The best way to test your changes is to run them locally and see how the will work before they are merged. You can check any formatting errors in real time and reduce the work load upstream. This requires that you have the repository locally and have some up to date version of Python installed.
Setting It Up
- While in the Docs repo directory:
pip install virtualenv # It has to be called venv because that's the name used in the .gitignore. # If you use any other name, your future pull requests will not be accepted. virtualenv venv # Then you need to enter the virtual environment # On Linux: source venv/bin/activate # On Windows: venv/bin/activate # use ``deactivate`` to get out of the virtual environment # Once inside, you need to install all of the requirements for the system. # Make sure you are inside the repository directory. pip install -r requirements.txt
Make Your Changes
Test Your Changes
- Inside the
docsdirectory, just abovesource, you will seeMakefileandmake.bat. While inside the virtual environment, you can use these to issue commands to Sphinx to build the documentation.
# Before each run to make sure the build environment is clean. make clean # Then build the html docs, we don't need anything else. make html
- Now go ahead and test your changes. You can open a file from the file browser or launcher a web browser from command line:
# Launch the index in Google Chrome google-chrome source/index.rst
- Double check that everything looks good. If it does, make your commits and Pull Request as outlined above.
- Inside the
Live preview¶
To see the changes as you type you can use this live preview editor. It does not format everything 100% correct but it formats things better than github. After you have wrote the page in the editor you can use the same methods described above. You will just have to paste in the code from the editor.